If...Then...ElseIf...Else...End If
The complete structure for VBA decision statements is:
If condition1 Then ' something if true ElseIf condition2 Then ' something else Else ' something else End If
To determine which button a user clicked on a message box, you can use a
variable of type vbMsgBoxResult:
Dim result As vbMsgBoxResult
result = MsgBox("Are you sure?", vbQuestion, "Verify")
If result = vbOK Then
msg = "You clicked OK."
Else
msg = "You clicked something other than OK."
End If
MsgBox msg
Possible values of the vbMsgBoxResult enumeration:
| Constant |
|---|
vbAbort |
vbCancel |
vbIgnore |
vbNo |
vbOK |
vbRetry |
vbYes |
For ... Next
Complete structure:
For i = start To end [Step stepSize] ' do something a few times, Step statement is optional Next i
Example: What is the output?
Dim i As Byte ' Byte cannot be larger than 256, good for small loops For i = 2 To 10 Step 2 msg = msg & i Next i MsgBox msg
For Each ... Next
The For Each structure is very helpful when iterating
through a collection, like a Range of cells, or Workbooks,
or ChartObjects.
Dim item As Object For Each item In Collection ' do something Next
Example:
Sub forEachExample()
Dim cell As Range
Dim counter As Integer
counter = 0
For Each cell In Range("Data")
If cell.HasFormula Then
counter = counter + 1
End If
Next
MsgBox "There are " & counter & " cells in the Data range that contain formulas."
End Sub
Do Loops: Do Until ... Loop, Do While... Loop, Do...Loop Until,
Do...Loop While
Explained in detail in text. Basic usage:
Do Until condition ' do something Loop
Example:
Dim isValid As Boolean
Dim password As String
isValid = False
Do Until isValid
password = InputBox("Enter a valid password:")
' put some code here so there won't be an infinite loop
Loop
Practice
You can practice some of the techniques in this lab by completing the samples below if you wish.
-
Write a subroutine that asks for two values of the Integer datatype and and determines which number is bigger. The output should be "The larger number is " followed by the larger number. Use an If statement in VBA, not any Excel worksheet functions. Use a third variable to store the largest value.
-
In the same file as Task 1, insert a new Module and call it PasswordTest. Use the code for the
Do Until ... Loopshown above to write a basic password testing sub. The password should be "wordpass". When the user enters the correct password, display a message box shown here (with the question mark):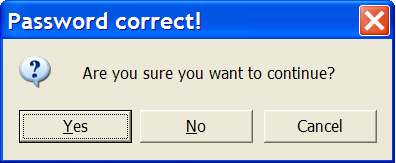
Windows Dialog 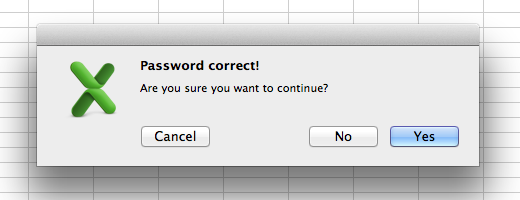
Mac Dialog If they click Yes, display a message about letting them continue. If they click No or Cancel, display a message saying they've decided to stop.
This message should have an Exclamation point icon such as:
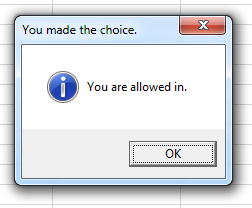
Windows XP Dialog 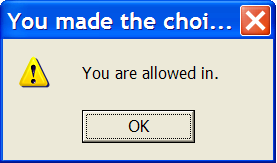
Windows 7 Dialog 
Mac OS X Dialog Mac msgboxes don't show message box styling.
Instructions
All tasks are to be completed on your own.
-
Save the spreadsheet file as a Macro Enabled Workbook (
.xlsm) file before you write more code. Name your spreadsheet with your network login followed by_l04.xlsm. For example, if your network login wasbarn4520, then your lab file should be namedbarn4520_l04.xlsm. Save often. -
Show the Developer Tab in Excel. Click File / Options Customize Ribbon and check the option for Developer Tab.
-
Put all code into a Module. Use a different Module for each task and name them appropriately as Task1 or Task2 etc.
-
Copy and paste this header into your code modules and fill it out:
Option Explicit ' ==== CP212 Windows Application Programming ===============+ ' Name: Your Name ' Student ID: ' Date: ' Program title: ' Description: '===========================================================+
-
Make sure you test your tasks before submitting your lab to be marked.
-
When finished upload your file to the Lab 4 Task Dropbox in MyLearingSpace to be marked.
Tasks
Download the file Passwords.xlsx which contains a single worksheet called Passwords, this sheet
has a list of all passwords currently used by students in column A starting in cell A1. Complete the
following tasks. Open the file and save it as a Macro Enabled Workbook
(file extension .xlsm). Name this spreadsheet with your
network login followed by _l04.xlsm. For example, if your
network login was barn4520, then the file should be named barn4520_l04.xlsm.
Remember to save your work frequently in case there are problems.
-
In the given file, write a subroutine that asks user to enter a new password using InputBox , embeded within a Do loop, to get a password. All passwords must be:
- eight characters long
- starting with an uppercase letter
- consist of uppercase letters
- no spaces
Examples of valid passwords: S6H191W4 , F59HD345 , G1TJNPC2
-
Check if the user enters a valid password
-
Expand your sub in (1) to include a second InputBox that asks the user to verify the password in the first input box. Embed the whole procedure within an outer Do loop. This outer loop keeps repeating until the user provides a valid password in the first InputBox and enters the same password in the second InputBox.
-
Now you have to compare the entered password with passwords given in the sheet. If the user selects one of these passwords, an appropriate warning maessage is displayed, and the user has to choose another password. When the user chooses valid password that is not being used, a "Congratulations" message should be displayed, and the new password should be added at the bottom of column A.
- To check the first character of the password, you can use:
ElseIf Not (Left(password1, 1) >= "A" And Left(password1, 1) <= "Z") Then isValid = False - To check remaining characters, you can use a for loop:
Else For position = 2 To 8 midChar = Mid(password1, position, 1) If Not ((midChar >= "A" And midChar <= "Z") Or _ (midChar >= "0" And midChar <= "9")) Then isValid = False Exit For End If Next
Hints:
Note