It is important that you have read through the text chapters on arrays before attempting the lab or at least have an understanding of arrays.
Sub ArraysExample()
' Declare an array of 6 pets
Dim pets(5) As String ' static array
Dim pet As Variant 'For Each control variables on arrays must be Variant
Dim zoo() As String ' dynamic array
pets(0) = "Cat"
pets(1) = "Dog"
pets(2) = "Fish"
pets(3) = "Snake"
pets(4) = "Lemur"
pets(5) = "Meerkat"
' Loop through the array, though can't extract the index number.
For Each pet In pets
MsgBox "The pet is a " & pet
Next
' Resize the zoo array to store 10 items
ReDim zoo(9)
End Sub
Sorting
We didn't discuss sorting in class but it is quite a large topic when dealing with computer programs and is linked to arrays. Sorting algorithms are a very large area of study. While it is possible to sort ranges of cells in Excel, you might not always be working in Excel (actually, even Word allows you to sort paragraphs) and it would be useful to know about different ways of sorting lists such as the Bubble Sort, Binary Sort, or Quick Sort (and there are many others). These techniques are important when working with arrays.
I'm presenting this file from John Walkenbach - Mr. Spreadsheets himself! - as a demonstration of the timing of various sorts, but have locked the code. If you want, check out his book for the solutions, but a good exercise it to write your own sort, like in Exercise 18b, page 202 of your text (pg 179 in 3rd edition). Sort Demo.xlsm
Searching
Searching for items in an array is also very common. Often the best way to search for an item requires that the list be sorted, so a lot of searching algorithms use data that has already been sorted using one of the methods discussed above. If you are trying to find an item in a range of cells, it may be faster to sort the range first, but in some cases you may not want the data sorted or changed. You either have to deal with poor search performance (ie, starting at the top and checking each item until you find your quarry - called a sequential search) or copy the data to a temporary location - like an array - sort it, then perform the search.
Loop Fill versus Array Fill
One quick note is that using an Excel array fill can be as much as 10x faster (or more!) than looping through an array 1 element at a time and writing the values into a cell. I tested this procedure with a value in 6000 rows and 3 columns and got 10x faster performance using array fill.
For example, if you had a 10x10 array (like a matrix) you can place the values on a worksheet with one command by setting a range of the right size and using the command:
TheMatrixRange.Value = myArray
Check out this example using a 20x10 array: TheMatrix.xlsm. You can see it visually takes longer, but you can add timing to see for yourself.
Remember, that you can easily create an array using the Array
function, though there are other techniques:
Dim weekdayGods As Variant ' Must be variant in this situation
weekdayGods = Array("Sun", "Moon", "Tiw", "Woden", "Thor", "Freya", "Saturn")
Practice
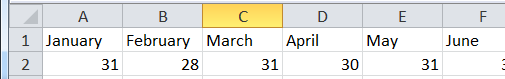
Download the file days.xlsx and use it for the following task. Read the names of the months from column A into an array called months, and the number of days in each month into an array called daysInMonth. On a new worksheet, output the names of the months in the first row of the spreadsheet starting in A1 and the number of days in the months starting at A2. Place a button on the worksheet to run your macro.
Fun
Sometimes I find examples that seem totally pointless, but they often demonstrate some creative thinking in how to use an application. Some examples are found below. Not all require VBA.
Spirograph.xls - A spirograph in Excel! Can you figure out how they did it? Contains no VBA.
Hypocycloid - animated.xls - another one from John Walkenbach, available on his web page: Animated HypoClycloid Charts (may run slowly)
Poker Simulation - from Chapter 34 of the text.
Blackjack.xls - Found on the net; comments and some code written in Portugese
Instructions
-
All tasks are to be completed on your own.
-
Show the Developer Tab in Excel. Click File / Options Customize Ribbon and check the option for Developer Tab.
-
Put all code into a Module. Use a different Module for each task and name them appropriately as Task1 or Task2 etc.
-
Copy and paste this header into your code modules and fill it out:
Option Explicit ' ==== CP212 Windows Application Programming ===============+ ' Name: Your Name ' Student ID: ' Date: ' Program title: ' Description: '===========================================================+
-
Make sure you test your tasks before submitting your lab to the Dropbox to be marked.
-
When finished upload your file to the Lab 5 Task Dropbox in MyLearingSpace.
Tasks
-
Download the file Airline_Flights_2023.xlsx and complete the following task. Open the file and save it as a Macro Enabled Workbook (file extension
.xlsm). Name this spreadsheet with your network login followed by_l05.xlsm. For example, if your network login wasbarn4520, then the file should be namedbarn4520_l05.xlsm. Remember to save your work frequently in case there are problems.The file Airline_Flights_2023.xlsx contains a list of flights in columns A,B, and C.These three columns contains the origin, the destinationand the flight number. You are interested in flights from any city in column E end in any city in column F. Write a subroutine that:
- Cell H1 contains label Origin, Cell I1 contains label Destination, and Cell J1 contains label Flight Number. All these three cells fonts should be bold, blue colored.
- Write a VBA code to find flights that are matching the search of desired origin and destination cities. Resulted flights shoul be listed in column H, I, and J.
- Place contents of Origin (of column A) in an array, contents of destination (of column B) in an array, and contents of Flight Numbers (of Column C) in an array.
- Place contents of Origin to be checked (of column E) in an array, and contents of Destination to be checked (of column F) in an array.
- The search mechanism should be as follows: start with the first city of the origin to be checked (ex. Pheladelphia). It has to be checked with the first city of destination to be checked (ex. Kansas City), if found, place the city names , and the flight number in columns H,I, and J respectively. Then search Philadelphia with Chicago and continue up to Seattle. Then, check New York with Kansas City, up to Seattle, and so on.
- Use mutiple For loops to do the search. The If conditions structure may be of the form:.
If Origins(k) = checkOrigins(i) And Des(k) = checkDes(j) Then
Or ypu can use your own search structure of any arrangement of loops and if structures
- Your results should look like:
- Clear the columns H, I, and J by writing a suitable subroutine. Use a command button to run this clear subroutine.
- Try your searching code on different set of origin and destination cities given in sheet Data2.
Hints:
Redim anyList(1 to anyListSize)
ReDim Preserve anyListlist(1 To listSize)